Exploring the CDR3 "Fingerprint Profile": Flexible IG/TR Target Combinations for Effortless Immune Repertoire Analysis
01 Background Overview
The immune system serves as the core defense mechanism against foreign and harmful invaders in the human body. As the "special forces" of adaptive immunity, B lymphocytes recognize antigens via B cell receptors (BCRs, i.e., immunoglobulins, IG), while T lymphocytes utilize T cell receptors (TCRs/TRs) to initiate precise immune responses. The collective diversity of functional BCRs and TCRs within an individual constitutes the immune repertoire. Its dynamic characteristics determine the breadth and efficacy of antigen recognition and response, while also reflecting the evolution of immune status. Deciphering the diversity of the immune repertoire is critical for unraveling immune mechanisms in infections, cancers, autoimmune diseases, and optimizing immunotherapeutic strategies.
IGs are tetrameric structures composed of two identical light chains (κ-IGK/λ-IGL) and two identical heavy chains (IGH) linked by inter-chain disulfide bonds (Figure 1.A). TRs are heterodimers formed by two different polypeptide chains: most TRs (∼95%) consist of α (TRA) and β (TRB) chains, while a minority (∼5%) comprise γ (TRG) and δ (TRD) chains (Figure 1B).
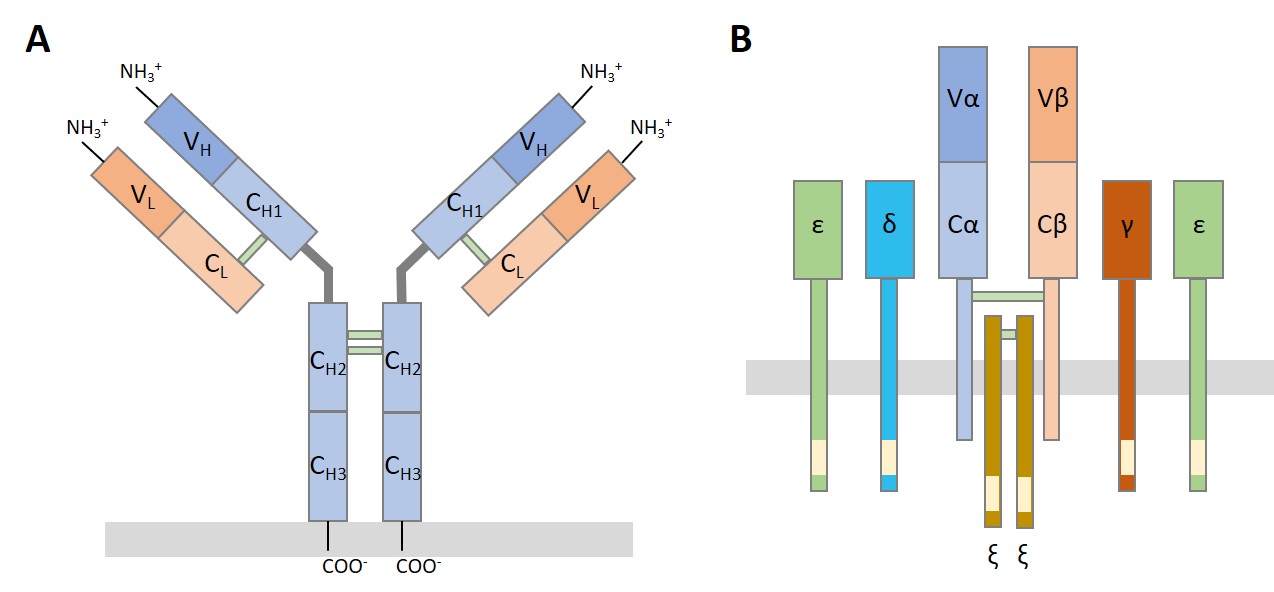
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of BCR/IG (A) and
TCR/TR (B) structures.
The N-nucleotides region of IG and TR molecules contains a highly variable
domain termed the variable (V) region, while the C-terminal region is
relatively conserved (constant region, C). Within the V-segments, three
hypervariable loops—complementarity-determining regions (CDR1, CDR2, and CDR3)—serve as antigen-binding domains. CDR1 and CDR2 are
encoded by only V-segments, whereas CDR3 is formed through V(D)J recombination,
involving the joining of V-genes with diversity (D)-, and joining (J)-segments.
Due to nucleotide insertions or deletions at V(D)J junctions, CDR3 exhibits the
highest diversity and directly interacts with antigens, making it the focal
point for immune repertoire analysis.
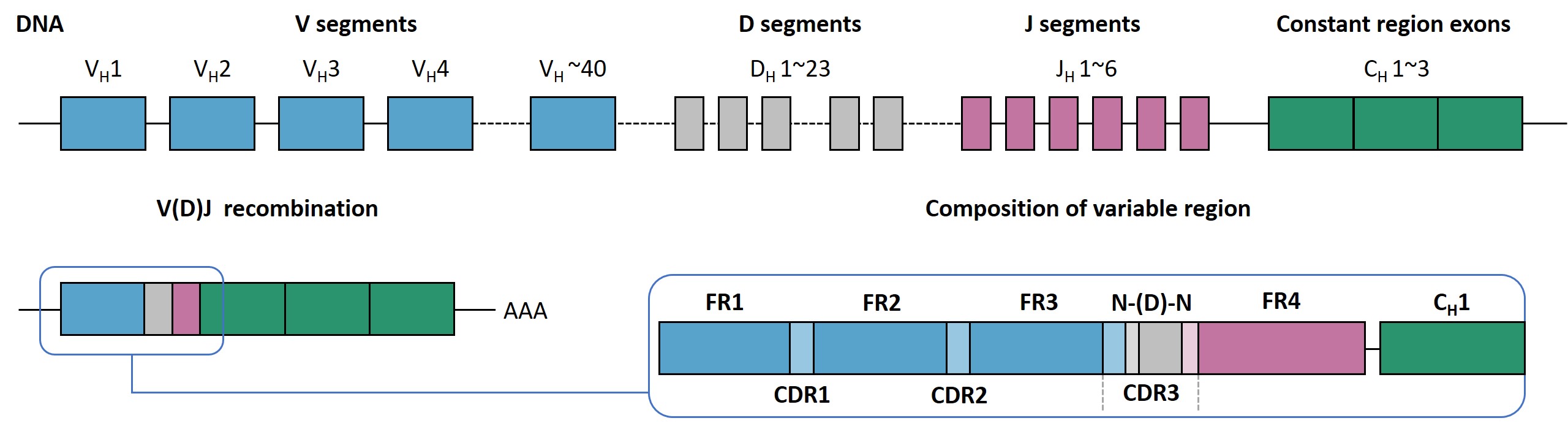
Figure 2. Structural basis of CDR3 diversity.
Nanodigmbio’s previously developed immune repertoire product, the IGTR
Panel v1.0, employs hybrid capture-based NGS to target pre-rearranged coding
regions of human IG/TR genes, enabling comprehensive analysis of DNA or
RNA-level rearrangements. However, methodological limitations prompted the
development of the NadPrep IGTR Multiplex PCR Library Prep Kit, which
enhances experimental efficiency, broadens application scenarios, and optimizes
cost-effectiveness.
02 Introduction
NadPrep IGTR Multiplex PCR Library Prep Kit is Nanodigmbio’s
first multiplex amplification-based library preparation kit. It utilizes
hundreds of primers targeting IGH, IGL, IGK, TRA, TRB, TRG, and TRD loci for adaptive immune antigen receptors to
efficiently enrich CDR3 regions across the immune repertoire, enabling precise
assessment of B and T cell diversity and clonality via NGS.
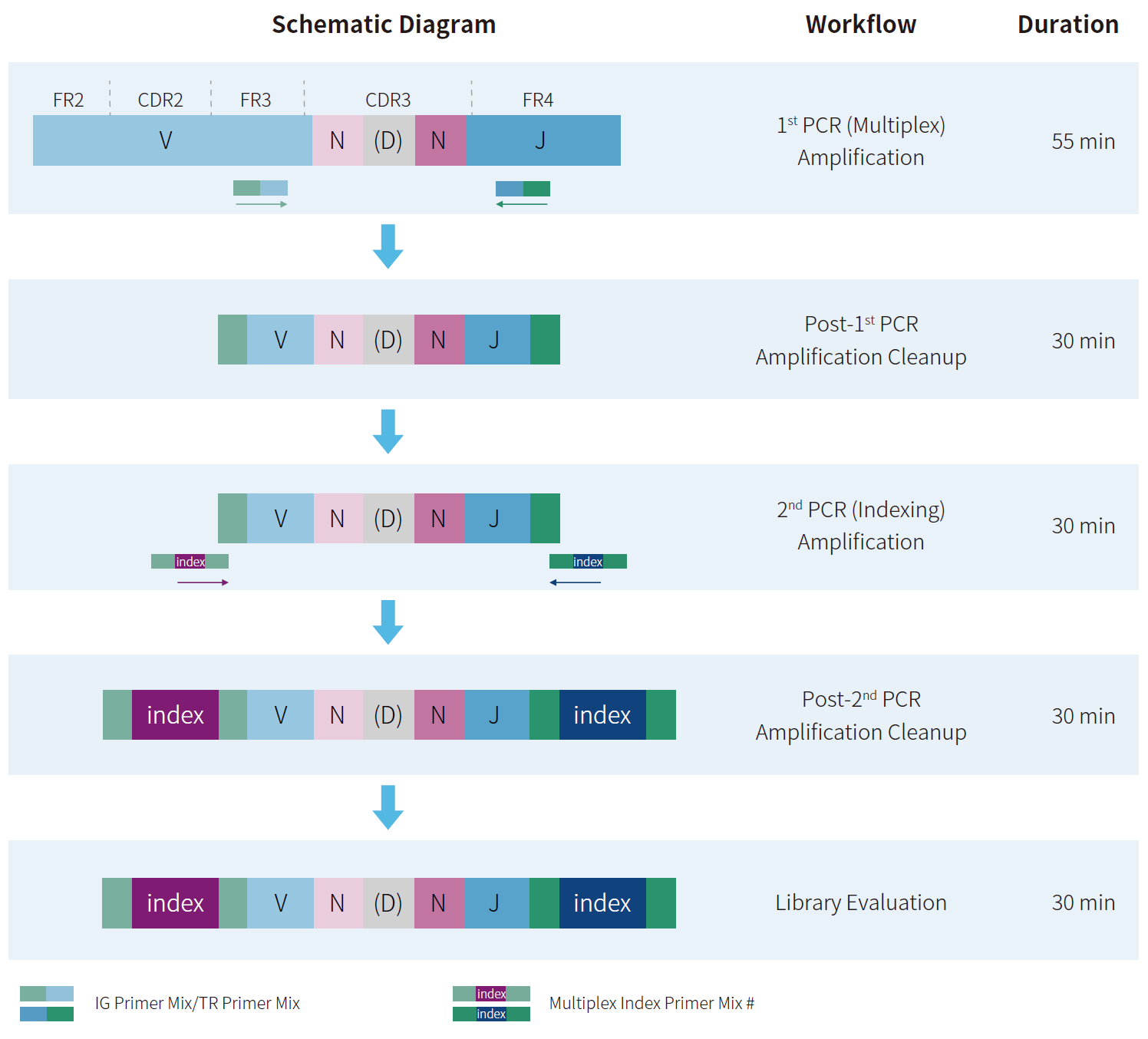
Figure 3. Workflow and experimental schematic.
Note: Libraries can be sequenced directly on Illumina® platforms or circularized
using the NadPrep Universal Circularization Kit v2 (Cat # 1002241) for MGI
platforms. PE150 sequencing is recommended.
2.1 Flexible Target Selection
The kit features modular primer design, offering two independent primer
mixes: IG Primer Mix (covering IGH/IGL/IGK) and TR Primer Mix (covering
TRA/TRB/TRG/TRD). Users can choose single-tube (IG or TR) or dual-tube (IG +
TR) workflows to focus on specific regions, reduce redundant data, and optimize
sequencing resource allocation.
2.2 Compatibility with Diverse Initial Samples
The kit supports 50-2000 ng of gDNA or cDNA. Optimal library yields are
achieved within this range. For inputs > 2,000 ng, splitting samples into
multiple reactions is recommended to maintain amplification efficiency. For
example, libraries prepared from 200 ng of leukocyte gDNA or cDNA exhibit
fragment distributions shown in Figure 4.
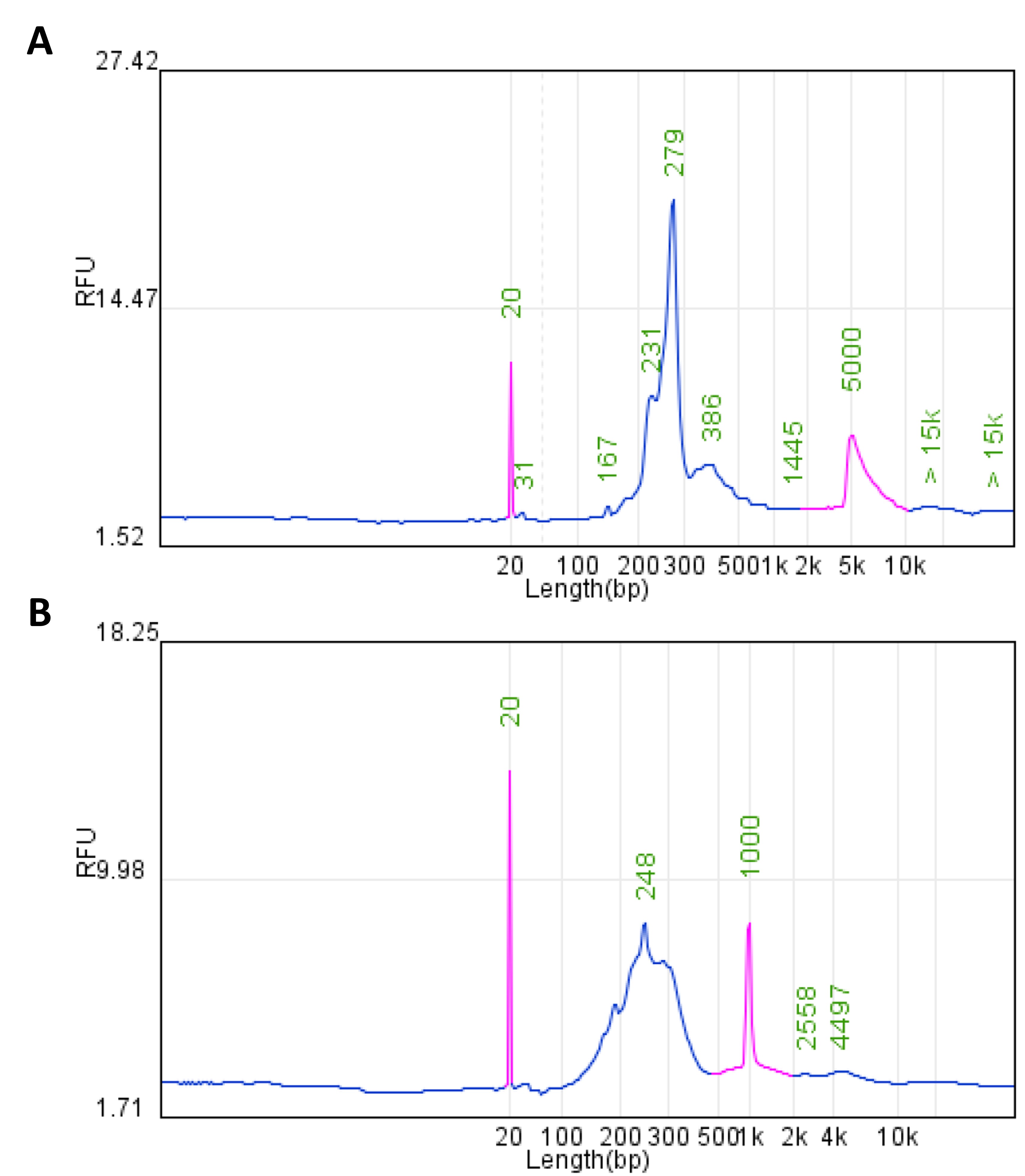
Figure 4. Library fragment distribution. (A) 200 ng leukocyte gDNA; (B) cDNA synthesized
from RNA.
03 Performance
Spiking 0.001% of a mixture of RAMOS and JURKAT
cell line gDNA into 2 μg leukocyte-derived gDNA, libraries were prepared using
this kit, with independent amplification (IG-only or TR-only) or combined
amplification (IG + TR). Sequencing data were analyzed using the companion
analysis tools to generate a clone list (Table 1.) and to evaluate cell
line-specific CDR3 sequences and read counts (Figure 5.). Results demonstrated
that the kit reliably detects low-frequency clones at 0.001%, achieves an
on-target rate of ~90% (i.e., the proportion of CDR3-associated reads relative
to total reads), and clearly distinguishes cell line-specific CDR3 sequences
and their read distributions, enabling clonality tracking and quantitative
analysis.
Table 1.
Clone list generated by analysis tools.
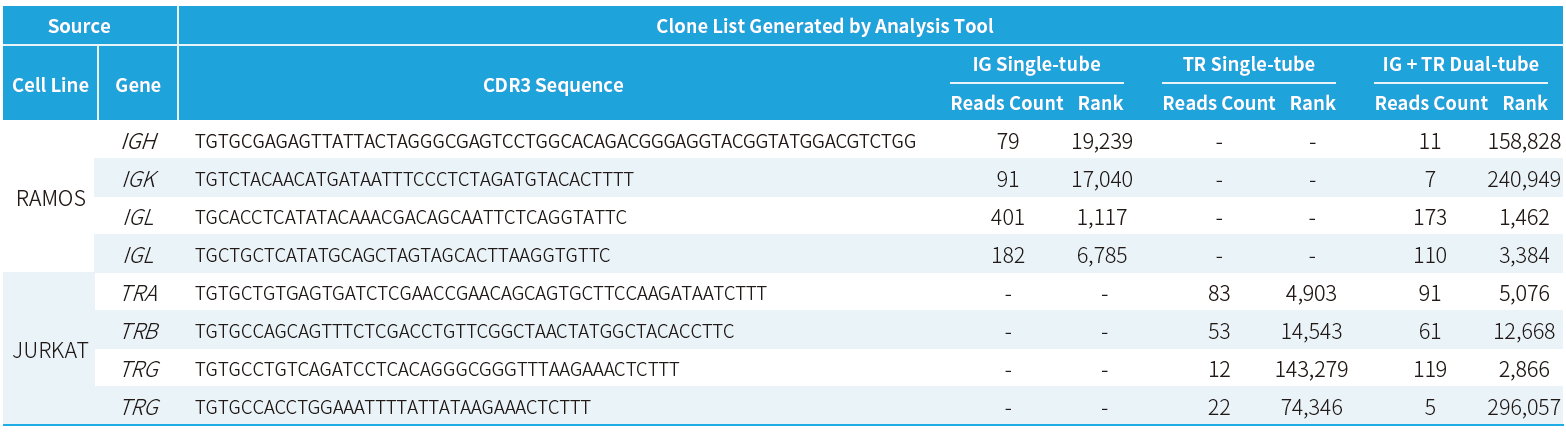
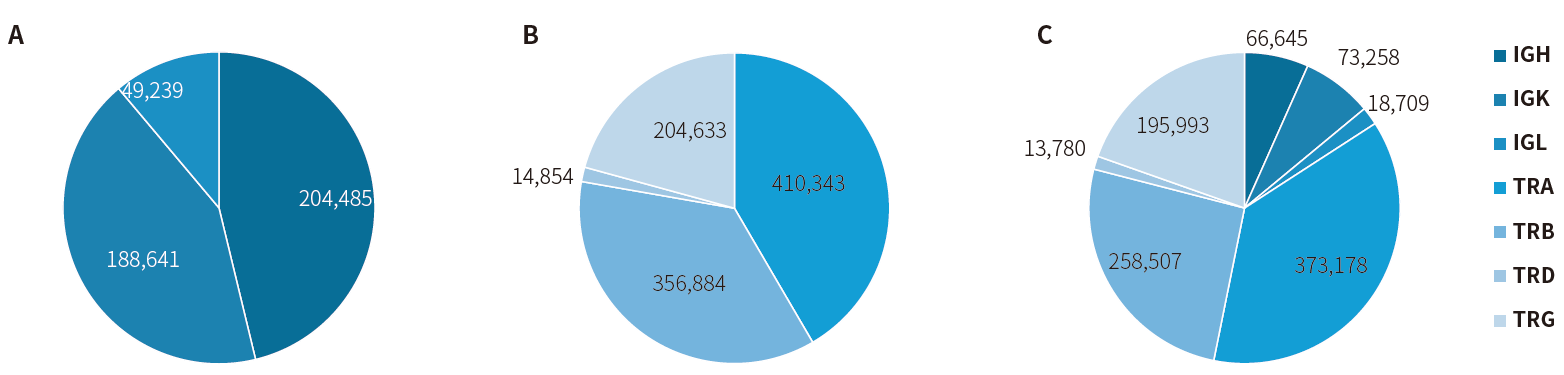
Figure 5.
CDR3 diversity analysis using the NadPrep IGTR Multiplex PCR Library Prep Kit. A. IG Primer Mix (single tube) (on-target: 86.49%); B. TR Primer Mix (single tube) (on-target: 93.36%); C. IG Primer Mix + TR Primer Mix (dual tubes) (on-target: 91.62%).
Note: Sequencing was performed on NovaSeq 6000 (PE150 mode) with a data volume of 2~2.4 Gb.
04 Applications and
Prospects
As a highly efficient multiplex amplification library preparation kit, this product enables enrichment of the CDR3 region in the human immune repertoire within as little as 3 hours. Users can flexibly select IG- or TR-specific enrichment modes based on research objectives, thereby reducing sequencing data volume while enhancing sensitivity for low-frequency clone detection. Whether applied to basic immune repertoire profiling, clonality analysis in lymphoid malignancies, or minimal residual disease (MRD) monitoring, this kit provides robust technical support for both research and clinical applications, facilitating efficient execution of complex immunological studies!
Solutions
- Methyl Library Preparation Total Solution
- Sequencing single library on different platform--Universal Stubby Adapter (UDI)
- HRD score Analysis
- Unique Dual Index for MGI platforms
- RNA-Cap Sequencing of Human Respiratory Viruses Including SARS-CoV-2
- Total Solution for RNA-Cap Sequencing
- Total Solution for MGI Platforms
- Whole Exome Sequencing
- Low-frequency Mutation Analysis
Events
-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Boston 2025 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG)

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio Invites You to Join Us at WHX & WHX Labs Kuala Lumpur 2025, Malaysia International Trade and Exhibition Centre in Kuala Lumpur

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio Invites You to Join Us at Hospitalar 2025, Brazil International Medical Device Exhibition in São Paulo

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Denver 2024 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG)

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Sapporo 2024 Annual Meeting of the Japan Society of Human Genetics (JSHG)

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Association for Diagnostics & Laboratory Medicine (ADLM)


