User Review | Nanodigmbio's Probe Capture-based HLA Typing Comprehensive Solution for the DNBSEQ Platforms
Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genes are among the most polymorphic regions in the human genome. HLA polymorphisms are associated with various diseases and play a crucial role in vaccine and drug target population screening, as well as tissue and organ transplantation. For example, the degree of HLA matching is a key factor in the success of organ, bone marrow, and stem cell transplantation. Additionally, HLA genotypes in cancer patients and somatic mutations in tumors can influence the effectiveness of immunotherapy. Therefore, HLA typing is of great significance in transplantation medicine, immune-related disease research, drug response studies, and platelet transfusion. Currently, the main HLA typing methods include sequencing-based typing (SBT), sequence-specific primer (SSP), sequence-specific oligonucleotide (SSO), and high-throughput sequencing.
Nanodigmbio’s HLA Typing Comprehensive Solution, based on probe-based liquid-phase hybridization capture, is fully compatible with MGI's DNBSEQ sequencing platforms (DNBSEQ-E25, DNBSEQ-G99, and MGISEQ-2000). Owning to Nanodigmbio’s extremely streamlined hybridization process and the high accuracy, sensitivity, ultra-low duplication, and minimal index hopping rate of the DNBSEQ platforms, the HLA typing throughput is significantly enhanced, delivering highly precise and reliable results.
01 HLA Typing Comprehensive Solution
Nanodigmbio’s HLA Typing Comprehensive Solution refers to the IPD-IMGT/HLA database, and targets 11 HLA genes (Class I: HLA-A, B, C; Class II: HLA-DPA1, DPB1, DQA1, DQB1, DRB1/3/4/5). By utilizing polymorphic probe combinations, the solution covers the full-length genome sequences of all alleles and supports high precision typing to the fourth field level.
The solution supports library preparation using the NadPrep Universal Adapter (MDI) Module, which provides 384 combinations of unique dual index (UDI) for the MGI’s DNBSEQ platforms, and the UDI combinations can be expanded to 768 options, ensuring high throughput even for large-scale sample processing. Additionally, our innovative NadPrep Universal Stubby Adapter (UDI) Module offers up to 768 UDI combinations, allowing a single library to be sequenced seamlessly on both MGI and Illumina platforms without conversion, thereby streamlining the experimental workflow.
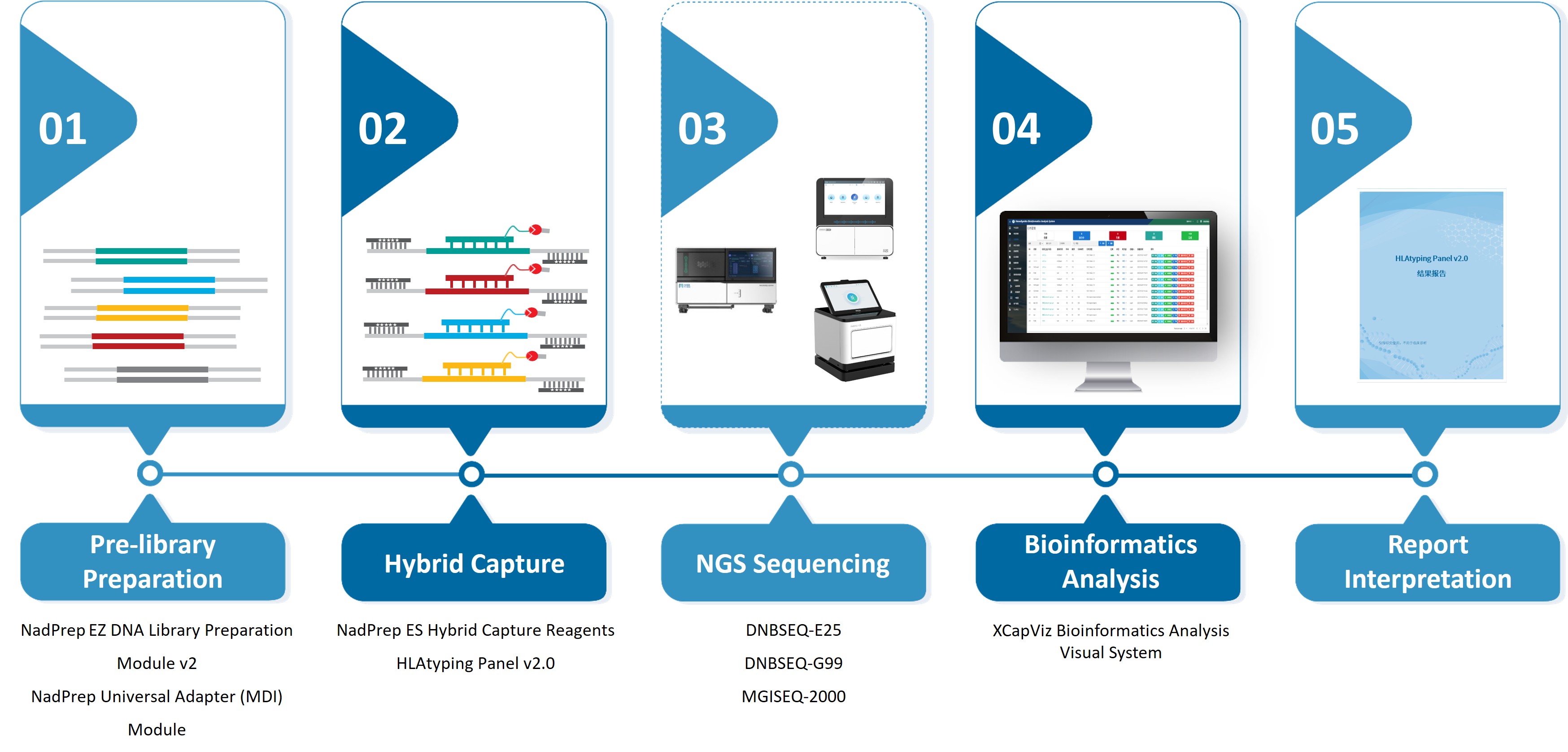
Figure 1. Nanodigmbio’s HLA Typing Comprehensive Solution.
02 Test Design
In this test, UCLA DNA Reference Panel (Class I & II) samples were used to prepare libraries with the NadPrep EZ DNA Library Preparation Module v2 and the NadPrep Universal Adapter (MDI) Module. Subsequently, hybrid capture was performed using the HLAtyping Panel v2.0 and NadPrep ES Hybrid Capture Reagents. The captured libraries were then sequenced on three sequencing platforms—DNBSEQ-E25, DNBSEQ-G99, and MGISEQ-2000—using a PE150 sequencing mode, with a raw data of 0.5 Gb per sample.
03 Test Results
The results showed that the data quality from all three sequencing platforms is excellent, with balanced GC distribution. The sequencing quality fully meets the analysis requirements.
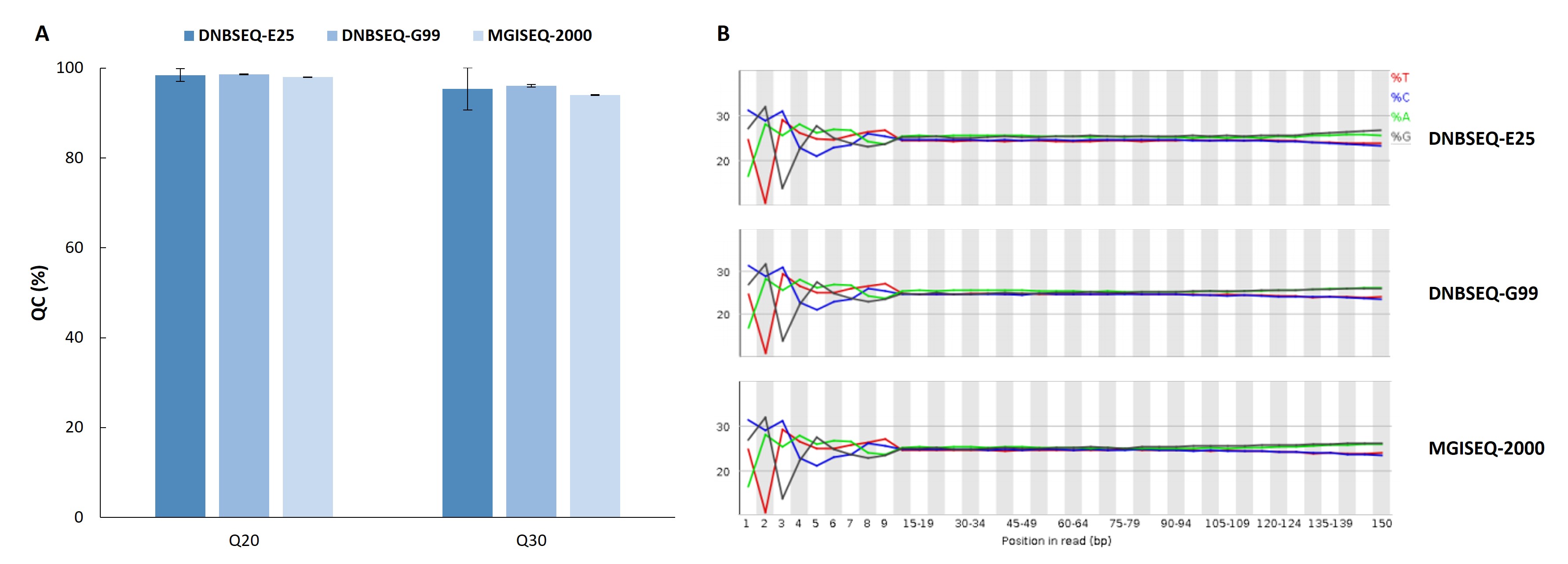
Figure 2. Sequencing quality performance of the Nanodigmbio’s HLA Typing Comprehensive Solution on the MGI’s sequencing platforms. A. Base quality scores; B. Base distribution.
Furthermore, the analysis of all three test datasets demonstrated excellent capture performance, with mappability exceeding 99% and on-target rates above 80%. It is important to note that the traditional metrics for assessing capture uniformity are not applicable in HLA typing scenarios, as certain regions of HLA genes exhibit high homology which may lead to abnormal uniformity metrics during QC analysis. Therefore, it is not recommended to focus on the performance of these indicators in sequencing-based HLA typing.
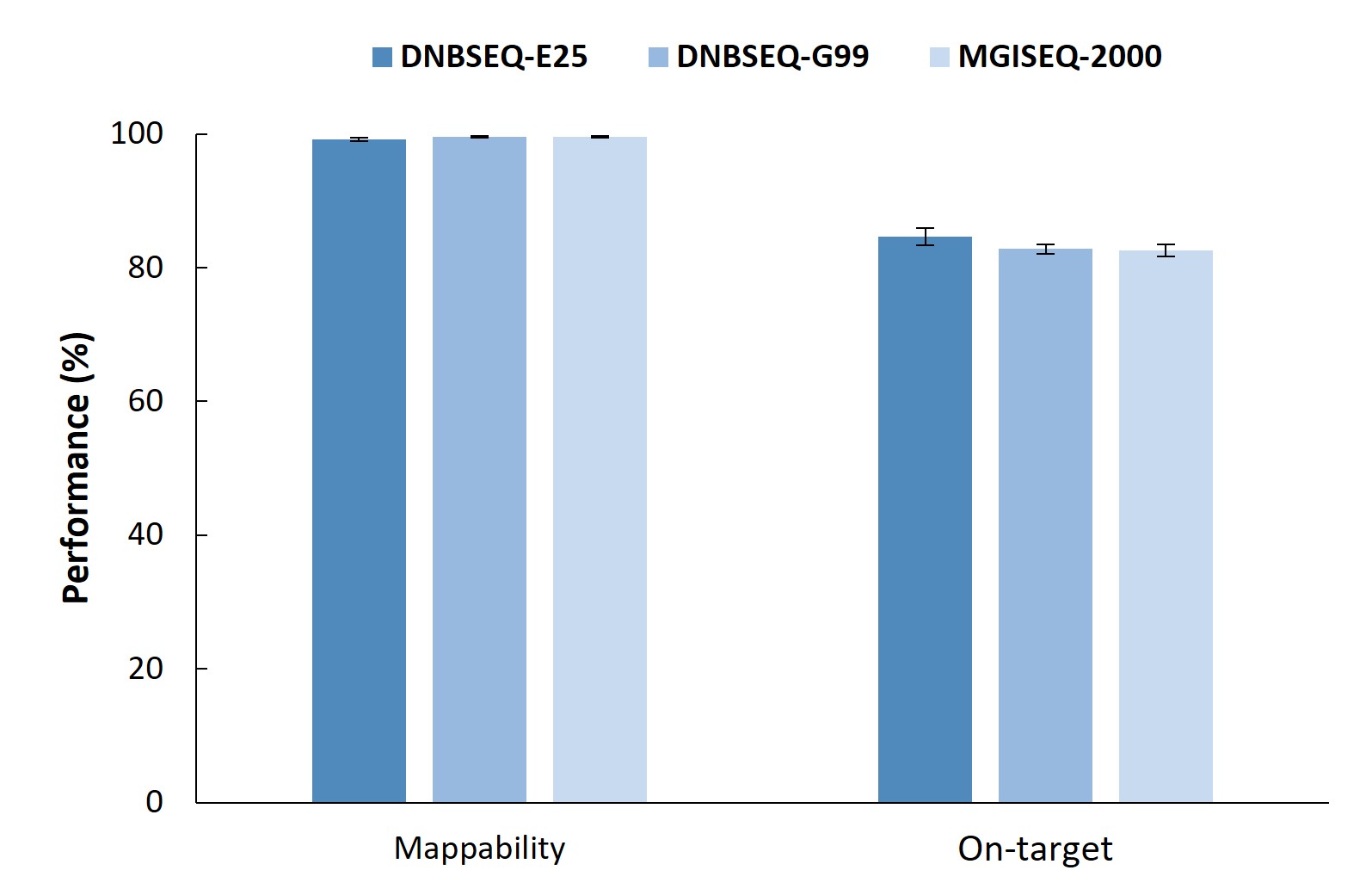
Figure 3. Capture performance of Nanodigmbio's HLA Typing Comprehensive Solution on the MGI’s sequencing platforms.
The raw data were analyzed using Nanodigmbio's XCapViz Bioinformatics Analysis Visual System, resulting in high-precision typing to the fourth field level. All test results were fully consistent with the reference results from the UCLA DNA Reference Panel samples (Table 1. and Table 2.).
Table 1. Typing results of Class I UCLA DNA Reference Panel.
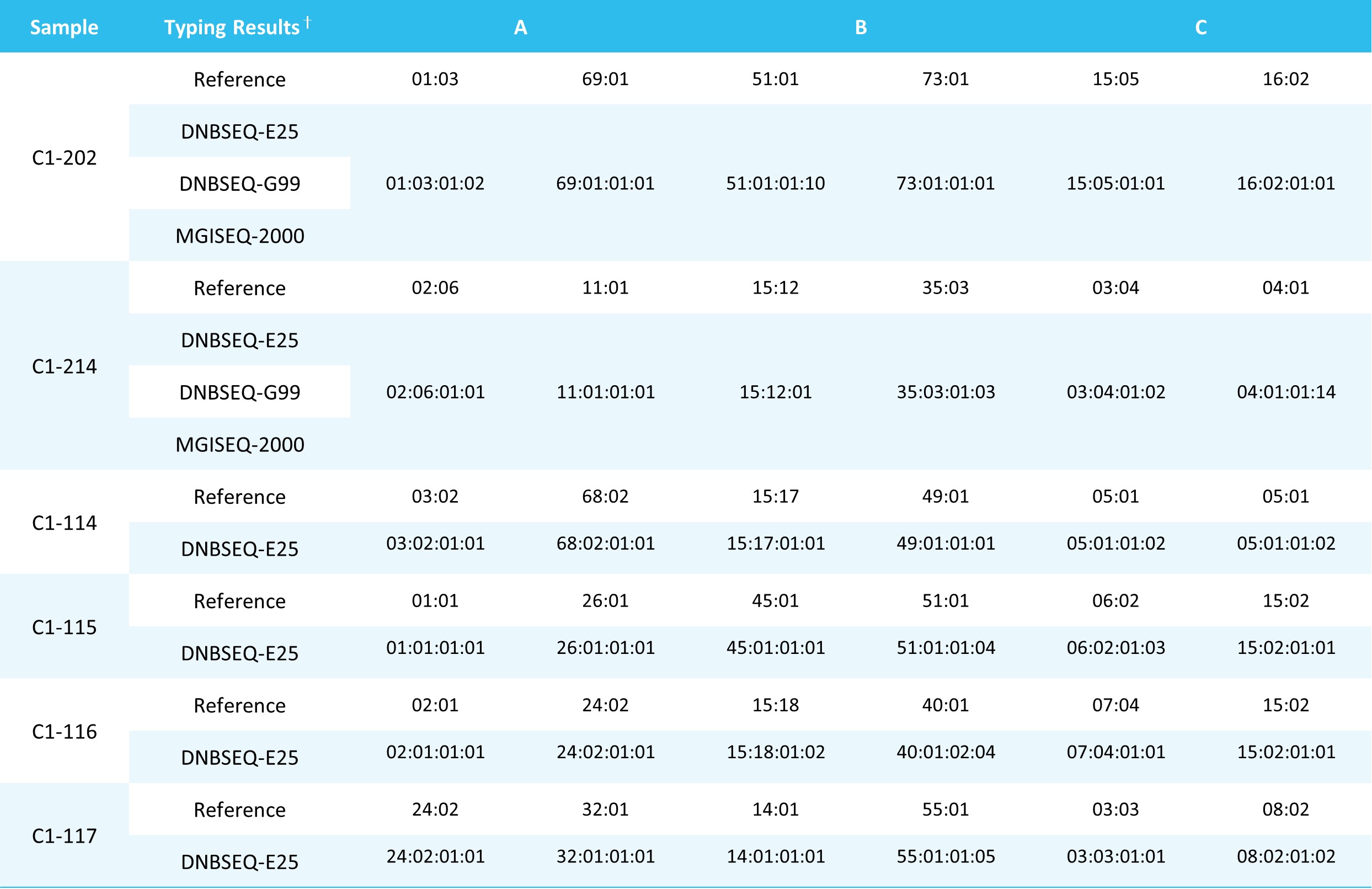
Table 2. Typing results of Class II UCLA DNA Reference Panel.
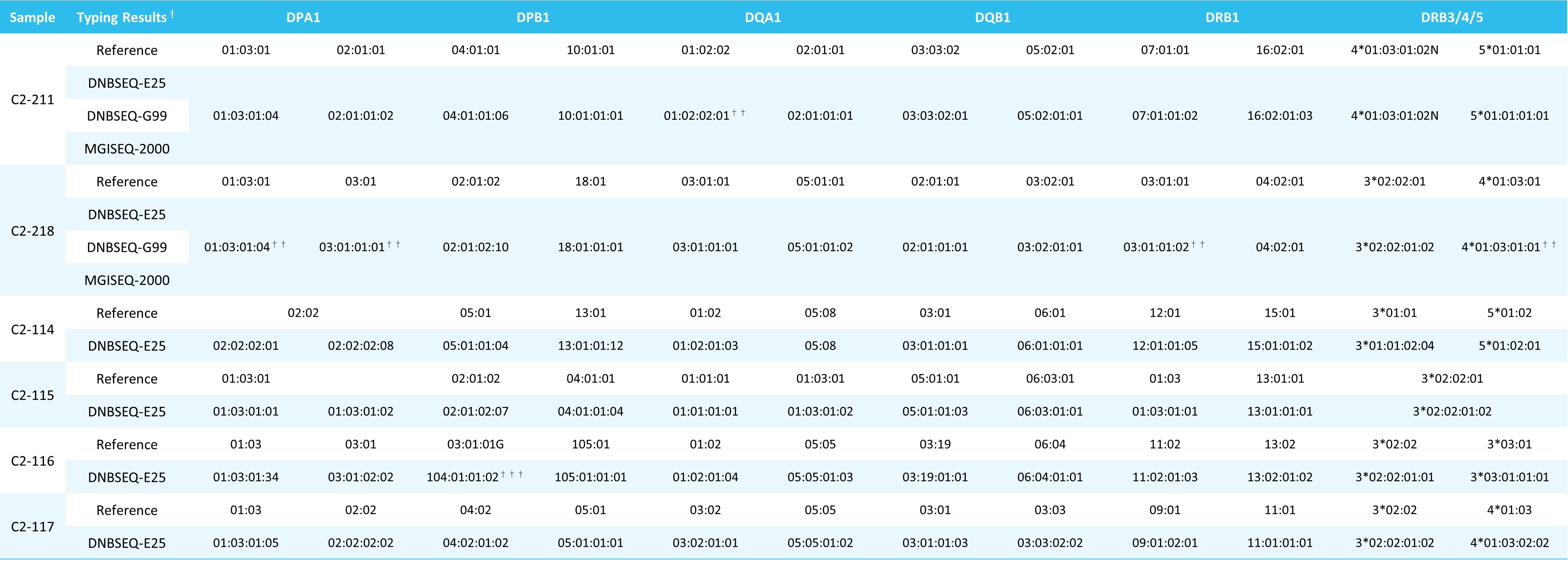
†: The reference typing results are provided by UCLA Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.
††: The fourth field typing results have been manually verified and corrected.
†††: According to DOI: 10.1016/j.humimm.2020.07.001, DPB1*03:01:01G and DPB1*104:01 are equivalent.
HLA genes are inherently high polymorphic, and the fourth field region is particularly variable. Significant nucleotide sequence differences in this region among individuals, coupled with numerous allele variations, make it highly challenging to accurately differentiate and determine specific genotypes. Additionally, the HLA intronic regions often contain repetitive sequences and segments that are similar to those in other regions. These repetitive and homologous sequences can lead to confusion during capture and alignment processes. In particular, during sequence alignment, repetitive sequences may cause the algorithms to erroneously align reads to similar but not actually corresponding regions, thus affecting the correct identification of alleles and increasing the risk of typing errors.
In this test, we observed fluctuations in automatic preliminary fourth field typing results for certain genes across different platforms in some reference samples. To investigate the cause of this phenomenon, we conducted an in-depth analysis.
For example, in the C2-218 reference sample, the preliminary result for DPA*01:03:01 showed two different fourth field typing: 04 and 31. After filtering the raw reads, we aligned them to the reference sequences for DPA*01:03:01:04 and DPA*01:03:01:31, respectively. Under strict no-mismatch conditions, we found that all three sequencing platforms consistently provided continuous coverage for the reference sequence of DPA*01:03:01:04, while the coverage for DPA*01:03:01:31 was discontinuous. Further analysis of the differential region revealed the presence of repetitive sequences that affected the alignment. Based on a comprehensive review of automated preliminary results and manual correction, the true typing for the C2-218 reference sample should be DPA*01:03:01:04.
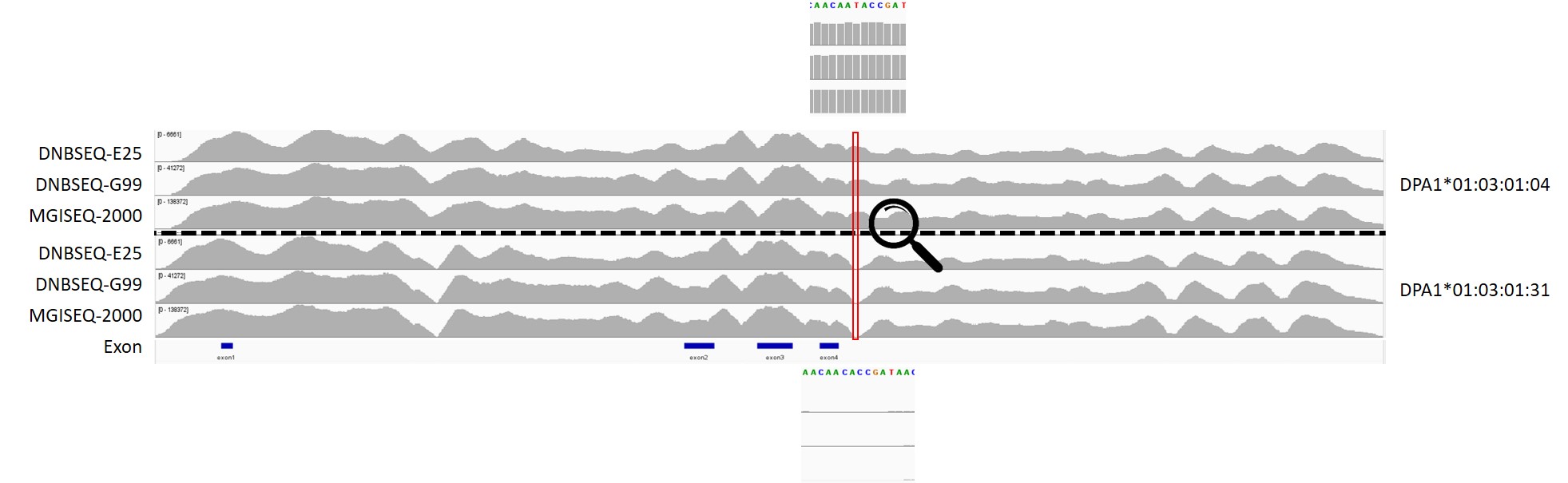
Figure 4. Manual correction of the fourth field typing results for DPA*01:03:01 in C2-218 reference sample.
Following the same approach, we verified the other genes with fluctuations in the fourth field preliminary typing results. The causes of these fluctuations were similar to the above example. For the C2-211 reference sample, which provided a fourth field typing results for the DRB4 gene, the results from all three sequencing platforms were completely consistent with the reference results. This indicates that the difficulty in fourth field typing is closely related to the characteristics of the corresponding gene and the specific genotyping sequence.
05 Nanodigmbio’s HLA Typing Comprehensive Solution
Feature
1. High-precision Fourth Field Typing
HLAtyping Panel v2.0 covers the full-length genomic sequences of all alleles (including UTR, Exon, and Intron), taking all types into account and supporting high-precision typing to the fourth field level.
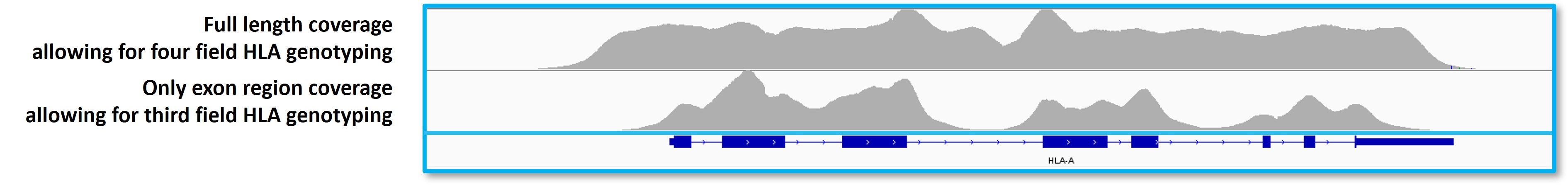
Figure 5. Full-length coverage of target genes by Nanodigmbio’s HLA typing Comprehensive Solution.
2. Polymorphic Probe Design with High Fault Tolerance
Compared to the primers used in multiplex amplicons, the probes used in liquid-phase hybrid capture offer higher fault tolerance. Refer to the IPD-IMGT/HLA database, Nanodigmbio has designed a large number of polymorphic probes with high fault tolerance, ensuring comprehensive coverage of all known reference sequences in the database.
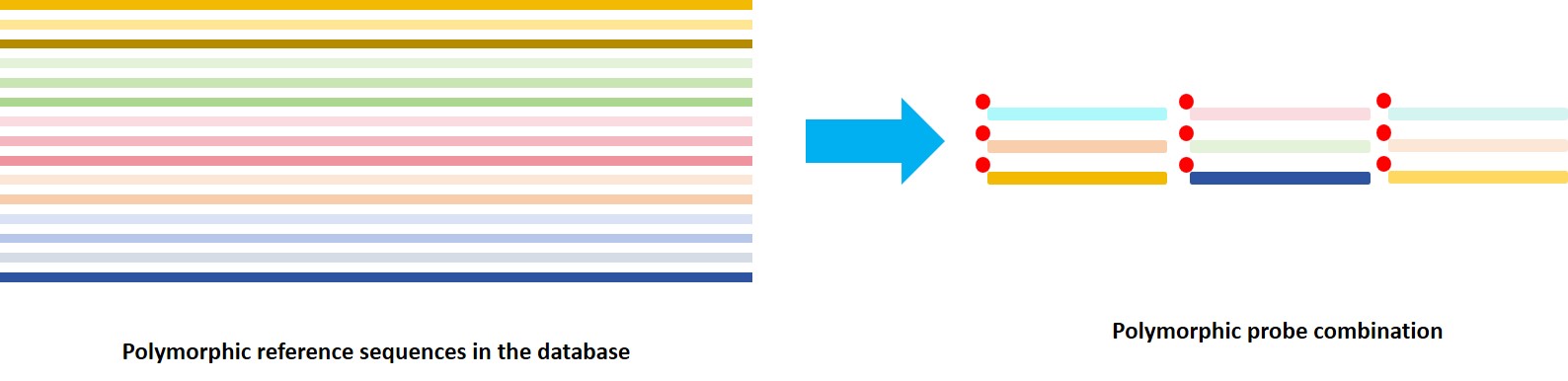
Figure 6. Polymorphic probes effectively capture
all reference sequences in the database.
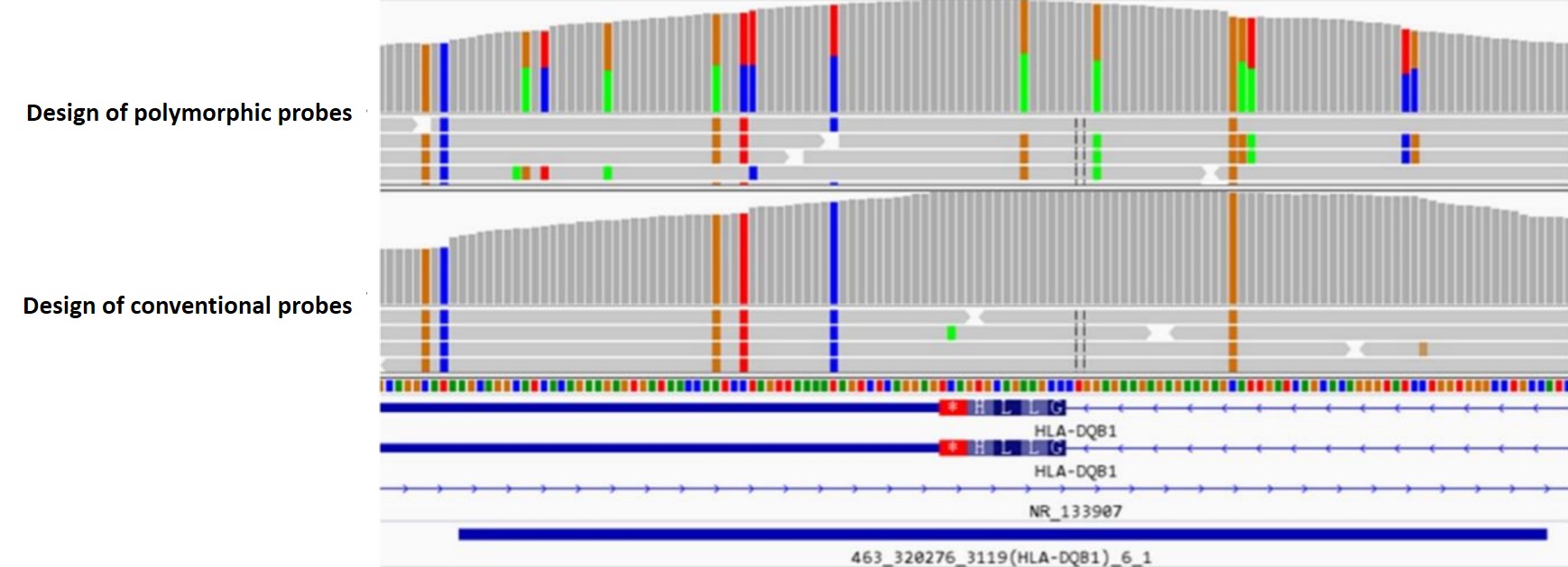
Figure 7. Compared to conventional probe designs, polymorphic probes provide more allelic information.
3. 30-min Rapid Hybridization with A Simplified Workflow
To minimize turnaround time (TAT) and enhance operational convenience, Nanodigmbio's HLA Typing Comprehensive Solution is specially provided with the newly optimized rapid hybrid capture system, NadPrep ES Hybrid Capture Reagents. The hybridization time has been shortened from 16 hr to 0.5 hr, and the number of Wash Buffers has been simplified from 5 to 1, allowing the entire wet-lab process from sample to sequencing to be completed within a single day. Additionally, the hybrid capture system supports multiplexing, enabling enrichment of up to 12 pre-libraries in a single hybridization reaction.
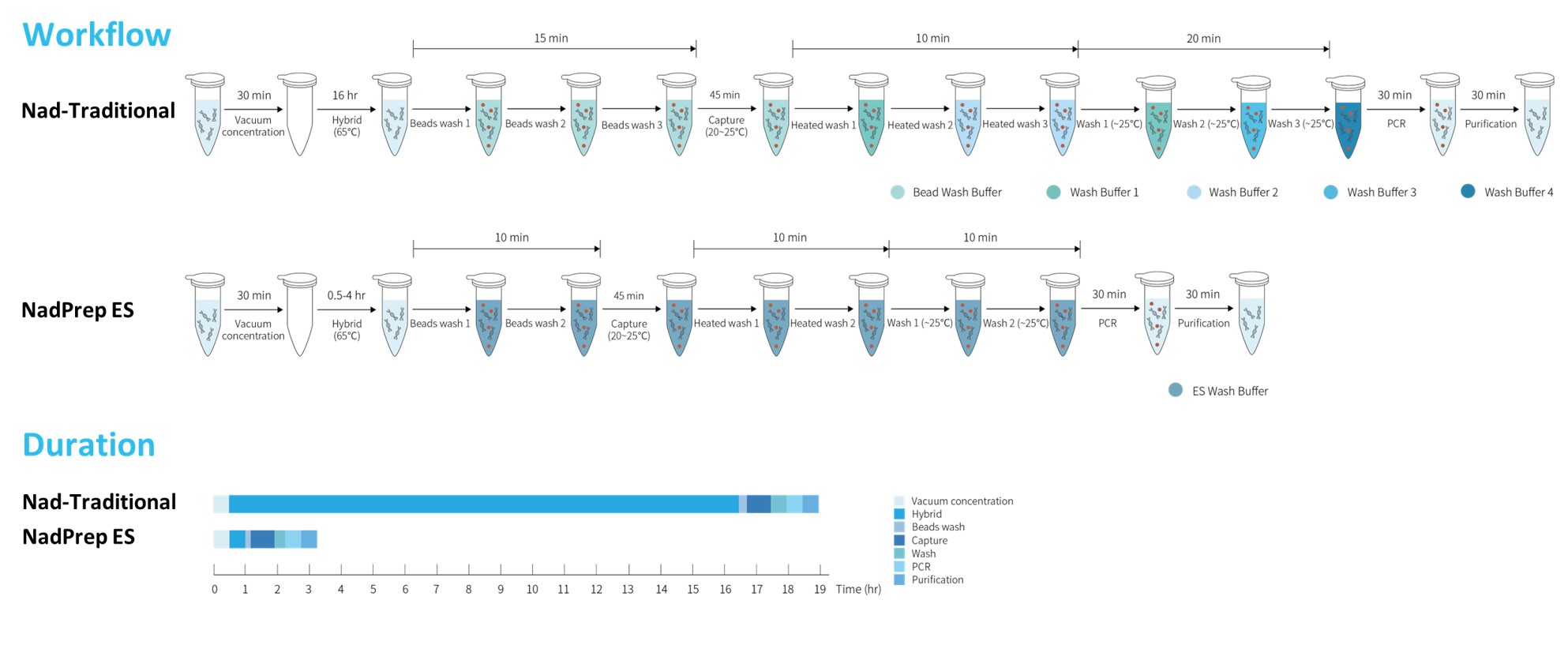
Figure 8. Workflow of NadPrep ES Hybrid Capture Reagents.
4. One-stop Bioinformatics Analysis to Overcome the DRB3/4/5 Typing Challenge
There are five common haplotypes for DRB. Open-source software like HLA-HD still requires manual interpretation of DRB haplotype data when analyzing the complex typing of DRB 3/4/5 gene. The XCapViz Bioinformatics Analysis Visual System not only accurately interprets conventional HLA gene typing but is also specifically optimized for DRB gene typing. It can automatically and correctly interpret DRB 3/4/5 gene typing based on common DRB haplotypes, thereby facilitating automated HLA typing.
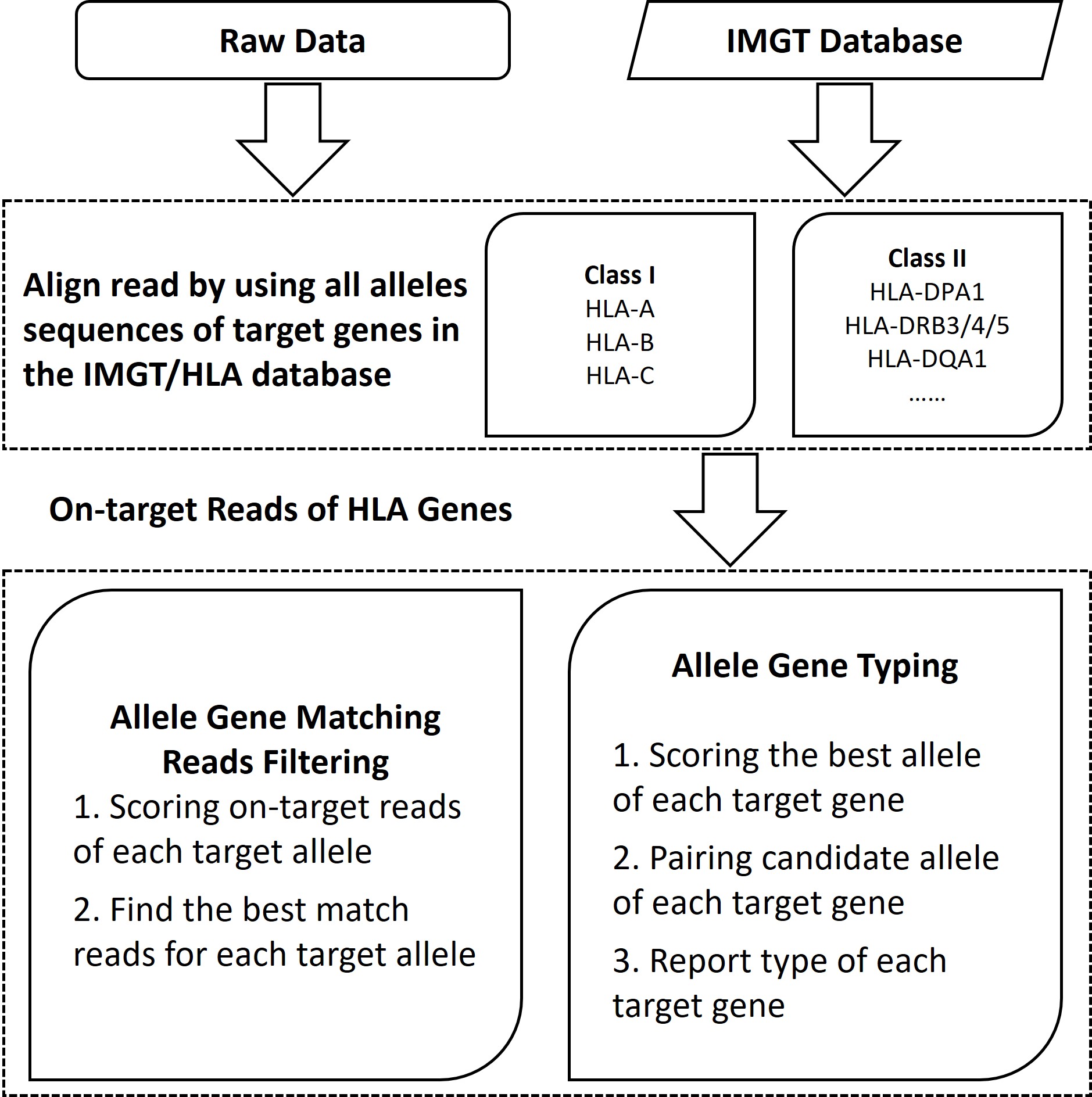
Figure 9. Principle of the HLA typing.
06 Summary
Nanodigmbio’s HLA Typing Comprehensive Solution, through its optimized design, has significantly shorten the time required for liquid-phase hybridization capture enrichment and simplified the operation workflow. When combined with the XCapViz Bioinformatics Analysis Visual System, it provides comprehensive sample-to-report support for high-quality HLA typing.
In tests using reference samples on three MGI’s sequencing
platforms, the solution demonstrated high typing accuracy. Notably, the
DNBSEQ-E25 is compact, flexible, and ready-to-use, offering fast and accurate
sequencing without the need for cleaning, perfectly meeting the demands of HLA
typing applications. The combination of these elements further optimizes the
TAT and brings more support for research in immunology, transplantation, and
other fields.
Product Information
|
Type |
Product |
Catalog# |
|
Nanodigmbio’s HLA Typing Comprehensive Solution |
NadPrep EZ DNA Library Preparation Module v2, 96 rxn |
1002602 |
|
NadPrep Universal Adapter (SI) Module Set E1 (for MGI), 96 rxn |
1003641 |
|
|
NadPrep Universal Adapter (MDI) Module Set E1 (for MGI), 96 rxn |
1003751 |
|
|
NadPrep Universal Adapter (MDI) Module Set E2 (for MGI), 96 rxn |
1003752 |
|
|
NadPrep Universal Adapter (MDI) Module Set E3 (for MGI), 96 rxn |
1003753 |
|
|
NadPrep Universal Adapter (MDI) Module Set E4 (for MGI), 96 rxn |
1003754 |
|
|
NadPrep NanoBlockers (for MGI, SI), 96 rxn |
1006205 |
|
|
NadPrep NanoBlockers (for MGI, DI), 96 rxn |
1006208 |
|
|
NadPrep ES Hybrid Capture Reagents, 96 rxn |
1005401 |
|
|
HLAtyping Panel v2.0, 96 rxn |
1001951 |
|
|
Sequencing Platforms |
DNBSEQ-E25 |
900-000490-00* |
|
DNBSEQ-G99 |
900-000561-00* |
|
|
MGISEQ-2000 |
900-000035-00* |
|
|
Sequencing Reagents |
DNBSEQ-E25RS High-throughput Sequencing Set (FCL PE150) |
940-000567-00* |
|
DNBSEQ-G99RS High-throughput Sequencing Set (G99 FCL PE150) |
940-001269-00* |
|
|
MGISEQ-2000RS High-throughput Sequencing Set (FCL PE150) |
1000012555* |
*For more details or to place an order, please visit the official MGI Tech website (https://www.mgi-tech.com/).
Solutions
- Methyl Library Preparation Total Solution
- Sequencing single library on different platform--Universal Stubby Adapter (UDI)
- HRD score Analysis
- Unique Dual Index for MGI platforms
- RNA-Cap Sequencing of Human Respiratory Viruses Including SARS-CoV-2
- Total Solution for RNA-Cap Sequencing
- Total Solution for MGI Platforms
- Whole Exome Sequencing
- Low-frequency Mutation Analysis
Events
-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Boston 2025 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG)

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio Invites You to Join Us at WHX & WHX Labs Kuala Lumpur 2025, Malaysia International Trade and Exhibition Centre in Kuala Lumpur

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio Invites You to Join Us at Hospitalar 2025, Brazil International Medical Device Exhibition in São Paulo

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Denver 2024 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG)

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Sapporo 2024 Annual Meeting of the Japan Society of Human Genetics (JSHG)

-
Exhibition Preview | Nanodigmbio invites you to join us at Association for Diagnostics & Laboratory Medicine (ADLM)


